Editor's note: This post has been updated in November 2024 for comprehensiveness.
Ever wondered how industrial sites keep communication flowing without relying on Ethernet cables? That’s where industrial Wi-Fi comes in, offering reliable wireless data connectivity in environments where cables either can't reach or won't hold up.
In this article, we’ll explore how industrial Wi-fi addresses these challenges, why it’s ideal for complex setups with moving equipment, and how it ensures crucial data flow between controllers and field devices for efficient operations. Let’s take a closer look at this essential technology and its practical applications.
In This Post:
History of Wi-Fi | How Does Industrial Wi-Fi Work? | The Benefits of Wi-Fi in Industrial Applications | Key Components of Industrial Wi-Fi Systems | Implementing Industrial Wi-Fi Solutions | Ensuring Security | Future Trends | Frequently Asked Questions
🔍 Explore Wireless Communication Products
Key Takeaways Industrial Wi-Fi systems are designed to handle specific, smaller data sets, such as sensor readings, equipment status, and machine data. This information is crucial for monitoring and controlling machinery, ensuring efficient factory operations. Transitioning to industrial Wi-Fi offers significant benefits, including cost savings, enhanced production efficiency, and improved visibility for monitoring potential issues.
|
A Brief History of Wireless Ethernet (Wi-Fi)

Image from FUTURE TREND FLOW
In the 1980s, the IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) developed the 802.11 standards for Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) communication. These standardized important parameters, for example, which frequencies in the wireless spectrum that should be used (2.4 GHz and 5.0GHz, etc.), and MAC and physical layer parameters.
In 1999, the Wi-Fi Alliance was formed, stating how the 802.11 standards are interpreted and improving cross-compatibility between wireless devices. In the image above, you can see how Wi-Fi (based on the 802.11 standards) has advanced with faster data transfer speeds, channel bandwidths, and antenna configurations over the years. The letter after 802.11 is used to denote the speed that each Wi-Fi-capable device is designed to handle.
How Does Industrial Wi-Fi Work?

Wi-Fi, a technology established and standardized over time, has become a familiar part of our daily lives, especially at home. A typical home setup involves a router connected to the internet, which uses Wi-Fi to wirelessly connect devices like smartphones, tablets, and PCs to both the internet and local networks. But how does Wi-Fi work in industrial environments? Manufacturers adapted this same technology for factories and made it more rugged and reliable for critical control systems. While industrial Wi-Fi relies on the same basic technology as home networks, the devices themselves and their implementation differ in key ways to meet the demands of the industrial world. Let's review some of the ways industrial Wi-Fi works.
Optimized for Industrial Data
Industrial Wi-Fi systems are optimized to focus on smaller and specific data. This data typically consists of control input readings (like pressure, temperature, and vibration from sensors), operational equipment data, or status data from machines that can be used for monitoring or controlling machinery and processes inside a factory.
Built to Withstand Harsh Conditions
Industrial Wi-Fi devices themselves are built to withstand harsh conditions. Unlike consumer-grade devices, industrial Wi-Fi components are designed with industrial-rated radios that can handle wide temperature ranges, resist shock, vibration, and electrical noise, and meet UL and hazardous location approval standards. They can also be mounted on DIN rails or within industrial enclosures and are powered by 24V DC, which is typical for industrial control systems.
Flexibility vs. Wired Infrastructure
In many industrial settings, using cables is impractical due to complex layouts or the risk of damage. Industrial Wi-Fi offers a flexible and resilient alternative to wired infrastructure, supporting seamless connectivity across various devices and systems. Technologies like industrial FL WLAN enable robust wireless communication, even in challenging conditions, and innovations such as self-healing mesh technology help maintain a reliable stream of data, enhancing operational efficiency.
The Result: Reliable, Flexible Connectivity
The result is a wireless system capable of providing reliable and consistent communication across a factory floor, enabling efficient operation of equipment and systems. By adapting familiar technology for rugged use, industrial Wi-Fi allows manufacturers to benefit from the flexibility of wireless connectivity while maintaining the reliability and performance that their operations demand.
The Benefits of Wi-Fi in Industrial Applications
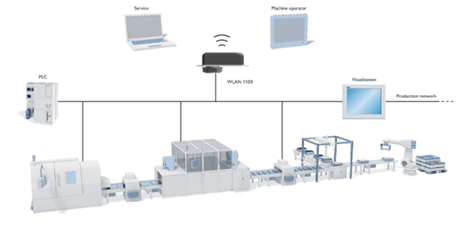 In industrial applications today, Ethernet communication is the default for connecting controllers (like PLC’s) to other field devices used to automate a system.
In industrial applications today, Ethernet communication is the default for connecting controllers (like PLC’s) to other field devices used to automate a system.
While you could connect all these devices via Ethernet cables, here are four main issues that can arise:
Higher costs
Cable costs quickly add up, making it expensive to run ethernet cables to devices.
Limited mobility
Many end devices (like robotic arms, AGV’s, etc.) need to move, and cables limit freedom of movement.
Difficult placement
Some places are just hard to get to for wiring.
Breakage
The more cables used, the greater the chance of them breaking, being snagged, or getting disconnected from their Ethernet switches.
This is where Industrial Wireless Ethernet (Wi-Fi) can really be a benefit. Products like Phoenix Contact’s Industrial Wi-Fi radio FL WLAN allows machine builders and end-users to implement a Wi-Fi network into their system for Ethernet network flexibility, freedom, and simplicity:
Flexibility
Industrial wireless systems provide reliable communication between the controller and autonomous transport systems, warehouse shuttles, or carry systems.
The Wi-Fi radio can be used as an Access Point, Client, or Repeater. You can use the Radio to make remote changes to the control system, collect data from machines to an upper-level network for IIoT purposes, or extend the Wi-Fi network in your industrial plant.
Design Freedom
Do you have AGV’s, Robots, or other devices that need to move and communicate constantly? Then, mount an industrial Wi-Fi radio onto the device, and problem solved!
Simplicity
Maximize your design and eliminate the time and expenses associated with cable installations.
Key Components of Industrial Wi-Fi Systems
Industrial Wi-Fi systems are built from several key components that work together to provide reliable and efficient connectivity.
These components include access points, wireless Ethernet bridges, and various antennas and accessories. Each of these plays a crucial role in establishing and maintaining robust wireless networks in industrial environments.
Access Points

Access points are fundamental elements in industrial Wi-Fi systems, serving as the primary means of establishing wireless connections among various devices. This connectivity is vital for real-time data sharing and operational efficiency, which are essential in modern industrial applications.
Their strategic placement is crucial to ensure optimal coverage and connectivity throughout the industrial environment.
Effective deployment of industrial Wi-Fi begins with thorough planning and understanding of site-specific requirements to position access points where they can provide the best signal strength.
Properly configured access points can significantly enhance the reliability and performance of industrial Wi-Fi networks, ensuring continuous and stable connections.
Wireless Ethernet Bridges

Wireless Ethernet bridges play a critical role in expanding the capabilities of industrial Wi-Fi networks by integrating wired devices into the wireless infrastructure.
These bridges are especially useful in dynamic industrial applications where machinery and equipment must move freely without being tethered by cables. Ethernet bridges, by linking wired devices to the wireless network, boost the flexibility and scalability of industrial Wi-Fi systems.
Antennas and Accessories
The performance of industrial Wi-Fi systems is heavily influenced by the quality and type of antennas used. A variety of antennas, including omnidirectional and directional types, are crucial for optimizing Wi-Fi performance in industrial settings. These antennas ensure that wireless signals can cover extensive areas and penetrate through obstacles, maintaining robust connectivity.
Accessories like surge protectors and connectors also play crucial roles in enhancing the reliability and efficiency of industrial Wi-Fi systems. These tools help protect the wireless infrastructure from damage and ensure consistent performance, which is critical for maintaining continuous operations in industrial environments.
Implementing Industrial Wi-Fi Solutions
Implementing industrial Wi-Fi solutions involves a systematic approach that includes site assessment and planning, installation and configuration, and ongoing maintenance and troubleshooting. Each step is needed to ensure the wireless network's reliable operation. Luckily, you don't have to go it alone.
Site Assessment and Planning
 A detailed site survey is crucial for setting up successful industrial Wi-Fi solutions. It involves both active and passive methods to assess the wireless environment and physical layout. These surveys determine optimal access point locations for robust coverage.
A detailed site survey is crucial for setting up successful industrial Wi-Fi solutions. It involves both active and passive methods to assess the wireless environment and physical layout. These surveys determine optimal access point locations for robust coverage.
Modern surveys use AI and machine learning for enhanced network planning, predictive modeling, and optimizing performance, considering building materials and device density. It's also essential to identify the number of devices to ensure the necessary network infrastructure.
Image from Field Engineer
Installation and Configuration
Proper installation and configuration of Wi-Fi equipment are crucial for compatibility and optimal performance, especially in industrial settings. Implementing a mesh Wi-Fi system enhances network resilience and coverage by strategically placing access points. Configuration should include security protocols, traffic management, and device connectivity to ensure reliable and efficient industrial operations.
Mitigating Radio Frequency Interference in Industrial Environments
Radio Frequency (RF) interference is a common challenge in industrial settings, especially with the presence of heavy machinery. Industrial Wi-Fi systems are designed with several strategies to mitigate RF interference and ensure reliable connectivity:
Pro Tip: Effective shielding, filtering, and choosing the right frequency band can prevent most RF interference issues.
Shielding
Metal Enclosures: Enclosing sensitive components in metal enclosures prevents RF signals from entering or escaping devices.
Shielded Cables: Braided copper shielding around cables protects signal transmission from external interference.
Filtering
Power Line Filters: These suppress conducted RF noise originating from the power supply.
Signal Filters: Specialized filters block specific frequencies within the radio circuitry, reducing interference.
Antenna Design and Placement
Directional Antennas: Focused radiation patterns direct signals to intended receivers, minimizing signal dispersion.
Antenna Placement: Positioning antennas away from major interference sources, such as motors or power cables, helps improve signal quality.
Advanced Technologies
Diversity Reception: Multiple antennas in different locations mitigate the effects of multipath interference, improving signal quality.
Adaptive Modulation and Coding (AMC): Adjusting transmission parameters in real-time optimizes performance in challenging environments.
Frequency Band Selection: Choosing less congested frequency bands, such as 5GHz, helps avoid interference from other devices operating on 2.4GHz.
Regulatory Compliance: Complying with electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) standards ensures Wi-Fi radios do not produce excessive interference.
Combining these strategies with careful network planning helps industrial Wi-Fi systems overcome RF interference, ensuring reliable connectivity for critical processes.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Reliable industrial Wi-Fi networks require ongoing maintenance and troubleshooting. Remote monitoring aids in predictive maintenance, detecting issues early, and minimizing downtime. Advanced diagnostics and support services help maintain a stable wireless infrastructure for continuous operations.
Ensuring Security in Industrial Wi-Fi Networks
Security is a paramount concern in industrial Wi-Fi networks. The latest wireless security protocol, WPA3, is recommended for strong network protection, providing enhanced security features to safeguard against unauthorized access. Implementing two-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security, requiring users to provide an additional code beyond just a username and password.
Other essential security measures include data encryption, MAC filtering, and disabling SSID broadcasts to make it more challenging for unauthorized users to identify and connect to the network. Regularly updating router firmware and utilizing strong passwords are crucial to maintaining a secure wireless network and mitigating security risks.
These precautions help companies safeguard the integrity of their industrial Wi-Fi networks, protecting sensitive information and ensuring reliable operations. However, they aren't the only precautions you can take. Contact your local Airline Sales representative to learn more. New to Airline? Contact our customer service team, who can connect you with an expert.
Future Trends in Industrial Wi-Fi
As technology continues to evolve, the future of industrial Wi-Fi looks promising, with several emerging trends. The growing adoption of IoT devices necessitates advanced network infrastructures to handle increased traffic and bandwidth demands. Wi-Fi 6, also known as 802.11ax, is designed to support a higher density of devices, improving network efficiency and capacity.
Wi-Fi 6 features enhancements like Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA), which allows multiple devices to communicate simultaneously, reducing latency and improving overall network performance. Additionally, the use of mesh networks improves connectivity by using multiple interconnected nodes, providing reliability and coverage across large areas.
These advancements will continue to drive the adoption of industrial wireless solutions, enabling smarter and more efficient industrial environments.
Industrial Wi-Fi is similar to the Wi-Fi you likely use every day, just ramped up and armored, enabling a smarter, more efficient, and cost-effective operation. Whether you use Industrial Wireless Ethernet today or not, you probably will soon.
With a digital future focused on the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), the use of smart devices like tablets and smartphones is becoming a common design element throughout industrial systems for setup, data acquisition, diagnostics, and maintenance.
If you have questions or need assistance with your Wireless Ethernet system, Airline Hydraulics has industry experts and wireless technologies that can help you meet your needs.
Resources and Information:
- Shop Wireless Communication Products
- Technically Speaking - Airline Hydraulics
- Airline Hydraulics YouTube Channel
- Wi-Fi 6 technology
Don’t forget to subscribe to our blog!
If you have a question or comment about this post, please leave it in the comments below!






%20copy.png)



Leave Comment