Have you ever gone to the hardware store and wandered down the fastener aisle?
If you have, you have probably been overwhelmed by the options, English or metric, fine threads or coarse, machine screws or wood screws. The options seem endless, and so are the chances of picking the incorrect nut, screw, or bolt for the job. Hopefully, your local hardware store is like mine, and there are knowledgeable associates ready to make sure you make the right selection.
This post is your virtual guide, embodying that knowledgeable hardware associate, ready to save you from the maze of options and help you make the right decisions for all your pneumatic valve, cylinder, and air tool needs. So, let's get into it and start reducing air leaks and confusion.
Jump to a Section
What Are Pipe Threads? | Understanding the Differences | Types of Pneumatic Pipe Threads
| SMC Pneumatic Survival Guide
What Are Pneumatic Pipe Threads?
In simple terms, pneumatic pipe threads are the connections that hold the various components in a pneumatic system together and allow compressed air to move through the system without escaping. They come in different sizes and shapes, each designed for a specific purpose and common in various parts of the world.
Now, why should you care about understanding these threads? Here's why:
![]()
Better Design: Knowing the right type of thread can help you design a more efficient and reliable system.![]()
Problem-Solving: Understanding the differences between these threads can help you troubleshoot issues when things go wrong, fittings break or leaks are found.![]() Cost Saving: Using the appropriate thread can reduce leaks, save on operating costs and reduce energy consumption.
Cost Saving: Using the appropriate thread can reduce leaks, save on operating costs and reduce energy consumption.
Understanding the Differences
When it comes to designing pneumatic systems, it is important to understand the distinctions between different types of pipe threads. These threads possess certain characteristics that directly impact their ability to create a tight seal, withstand mechanical stress, and meet the needs of different applications.
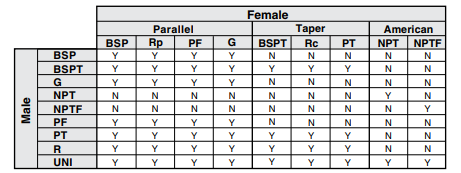
One key aspect is ensuring compatibility and interchangeability between components. Standards around pipe threads, like NPT (National Pipe Tapered), BSPP (British Standard Pipe Parallel), BSPT (British Standard Pipe Tapered), and others, aim to ensure that parts fit together correctly and form a tight seal. If incompatible threads are used, it can result in poor connections that may lead to leaks or component failure. Additionally, various countries and regions have their own thread standards, like Japanese Industrial Standard Taper Pipe Threads (PT), and American National Standard Taper Pipe Threads (NPT).
Another important consideration is the sealing efficiency. Certain thread types, particularly tapered ones like NPT, are designed to create a seal by the interference fit between the male and female threads. This is crucial in pneumatic systems, where air pressure must be maintained consistently. A proper seal prevents air leakage, which can compromise the system's efficiency and performance.
Types of Pneumatic Pipe Threads
A thorough understanding of different pipe thread types is necessary to ensure the reliability, safety, and maintenance requirements of pneumatic systems. This knowledge not only plays a critical role in designing the system and selecting the right components but also guarantees optimal performance while minimizing the risk of any potential issues.
BSPT Threads
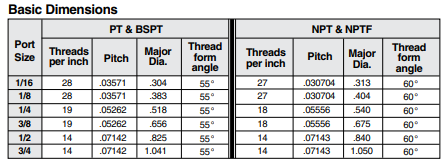
British Standard Taper Pipe Threads (BSPT) are widely used in Europe and Asia due to their reliable performance. These threads feature a 55-degree taper angle on internal and external threads, ensuring a secure and tight joint. Unlike other tapered pipe threads, BSPT incorporates a unique parallel bonding design between the sealant and the thread. This innovative feature prevents the sealant from being pushed inside the pipe, eliminating the risk of blockages and ensuring smooth flow. With BSPT, you can trust its efficient sealing capabilities and maintain uninterrupted operations.
PT Threads
Japanese Industrial Standard Taper Pipe Threads (PT) are extensively utilized in Japan. These threads also have a taper angle of 55 degrees, but have a unique characteristic of having two variations: taper external threads (R (PT)) and taper internal threads (Rc (PT)).
Unlike other tapered pipe threads, PT threads require the application of sealant to ensure a pressure-tight joint. This feature enhances the reliability and effectiveness of these threads, providing a secure and durable connection for various industrial applications.
NPT Threads
American National Standard Taper Pipe Threads (NPT) are North America's most commonly used pipe threads. NPT threads have a 60-degree taper angle and require the use of sealant to create a pressure-tight joint. NPT threads are often preferred because they offer better sealing capabilities than other commonly used parallel threads.
NPTF Threads
American National Standard Dry Seal Pipe Threads (NPTF) are another variation of NPT threads. The difference lies in its design, where the points of the crests of the threads are crushed into the roots of the mating threads to achieve a pressure-tight joint without the use of sealant. However, it is still recommended to use a lubricant or sealant to prevent galling of the threads.
PF Threads
Japanese Industrial Standard Parallel Pipe Threads (PF) are straight threads commonly used in Japan. These threads have a 55-degree taper angle and rely on a gasket or O-ring to ensure a pressure-tight joint. Due to their reliable sealing capabilities, PF threads are widely utilized in various industrial applications across different sectors in Japan. Because these threads rely on a gasket or O-ring to create a seal, the mating surface between the male and female components must be relatively flat to allow for a complete gasket seal.
Understanding the distinctions between pipe threads will make designing pneumatic systems much easier and result in a better, more energy-efficient system. Choosing the right fitting and sealant for BSPT, PT, NPT, NPTF, or PF threads ensures a secure joint, enhances system efficiency, and reduces the risk of leaks. Need support? we are always here to help. Contact us!






Leave Comment